In this post I'm going to shows the way of customize the ASP.NET identity match with our own business scenario.When you create the MVC application using default template in Visual Studio, it creates the schema using code-first method for authentication and authorization. In this post I'm going to show how customize the role entity, user entity and use our own database for the schema. First create the empty MVC project like in below.
public class CustomIdentityUser : IdentityUser
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
Following shows CustomIdentityRole class. In here Description added to the custom role class.
public class CustomIdentityRole : IdentityRole
{
public string Description { get; set; }
public CustomIdentityRole()
{
}
public CustomIdentityRole(string roleName, string description) : base(roleName)
{
this.Description = description;
}
}
After that create custom DB context as shown in below.
public class CustomIdentityDbContext : IdentityDbContext{ public CustomIdentityDbContext() : base("connectionString") { } }
Then create new database and create the connection string in web.config file as shown in below. In this example my custom DB name is CustomIdentityDb.
After these steps create OWIN startup class like shown in below. Go to add new items under project and add startup class. This class configure authentication scheme and uses cookie based authentication method in here. Path string point to the security controller action.
public class OwinStartup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
CookieAuthenticationOptions options = new CookieAuthenticationOptions();
options.AuthenticationType = DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie;
options.LoginPath = new PathString("/security/Register");
app.UseCookieAuthentication(options);
}
}
After create OWIN start up class should creates model classes needs for view pages. Model class creates under model folder in project template which are Login and Register.
public class Login
{
[Required]
[Display(Name = "User name")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Password")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Remember me?")]
public bool RememberMe { get; set; }
}
public class Register
{
[Required]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Required]
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "The password and confirmation password do not match.")]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; }
[Required]
[EmailAddress]
public string Email { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
In these models uses basic validation against model properties. Next step is creation of Security controller. Following code snippets shows security controller which contains the login, logout and register actions. Login and register action contains with GET and POST actions. In this application create another controller called ''Home" and redirect success logins to that controller.
public class SecurityController : Controller
{
private UserManager userManager;
private RoleManager roleManager;
public SecurityController()
{
CustomIdentityDbContext db = new CustomIdentityDbContext();
UserStore userStore = new UserStore(db);
userManager = new UserManager(userStore);
RoleStore roleStore = new RoleStore(db);
roleManager = new RoleManager(roleStore);
}
// GET: Security
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Register()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Register(Register model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
CustomIdentityUser user = new CustomIdentityUser();
user.UserName = model.UserName;
user.Email = model.Email;
user.FirstName = model.FirstName;
user.LastName = model.LastName;
IdentityResult result = userManager.Create(user, model.Password);
if (result.Succeeded)
{
userManager.AddToRole(user.Id, "Administrator");
return RedirectToAction("Login", "Security");
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("UserName", "Error while creating the user!");
}
}
return View(model);
}
public ActionResult Login(string returnUrl)
{
ViewBag.ReturnUrl = returnUrl;
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Login(Login model, string returnUrl)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
CustomIdentityUser user = userManager.Find(model.UserName, model.Password);
if (user != null)
{
IAuthenticationManager authenticationManager = HttpContext.GetOwinContext().Authentication;
authenticationManager.SignOut(DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ExternalCookie);
ClaimsIdentity identity = userManager.CreateIdentity(user, DefaultAuthenticationTypes.ApplicationCookie);
AuthenticationProperties props = new AuthenticationProperties();
props.IsPersistent = model.RememberMe;
authenticationManager.SignIn(props, identity);
if (Url.IsLocalUrl(returnUrl))
{
return Redirect(returnUrl);
}
else
{
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Invalid username or password.");
}
}
return View(model);
}
[HttpPost]
[Authorize]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult LogOut()
{
IAuthenticationManager authenticationManager = HttpContext.GetOwinContext().Authentication;
authenticationManager.SignOut();
return RedirectToAction("Login", "Security");
}
}
}
Now creates views for the login and register actions using scaffolding. After these steps create helper class for the role creation and call it from application start.
public static void CreateRoles()
{
CustomIdentityDbContext db = new CustomIdentityDbContext();
RoleStore roleStore = new RoleStore(db);
RoleManager roleManager = new RoleManager(roleStore);
if (!roleManager.RoleExists("Administrator"))
{
CustomIdentityRole newRole = new CustomIdentityRole("Administrator", "Administrators can add, edit and delete data.");
roleManager.Create(newRole);
}
if (!roleManager.RoleExists("Operator"))
{
CustomIdentityRole newRole = new CustomIdentityRole("Operator", "Operators can only add or edit data.");
roleManager.Create(newRole);
}
}
Let's test the application now. After you first run the application all tables needs for operate ASP.NET identity creates in DB. Following shows images of testing of this application.
 |
| Database table |
 |
| Registration view with custom fields |
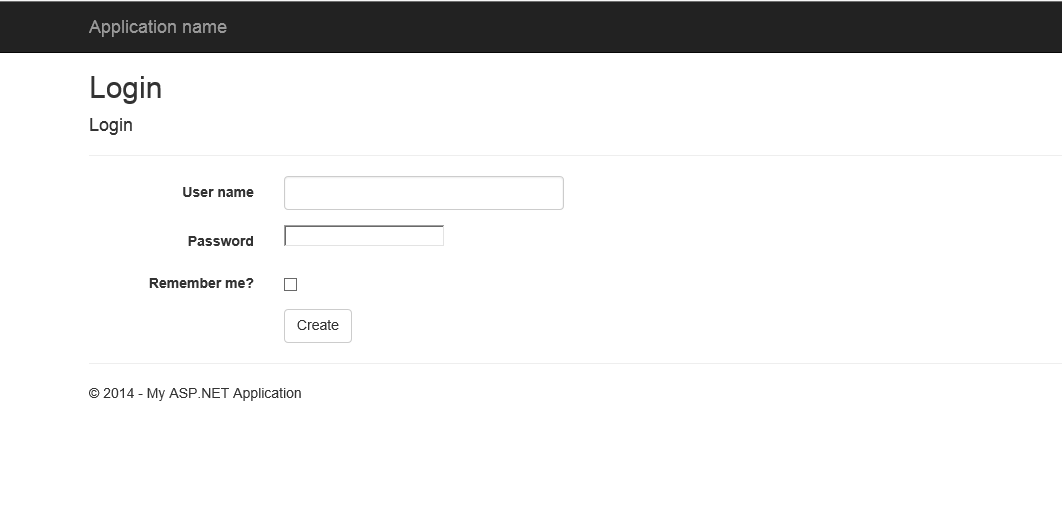 |
| Login view |


![1_thumb[3] 1_thumb[3]](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-TvoKgpKARmI/VpKK-HCHgNI/AAAAAAAAArs/d091R1a5b54/1_thumb%25255B3%25255D_thumb%25255B2%25255D.png?imgmax=800)
![2_thumb[1] 2_thumb[1]](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/--AwPoWqC5Ag/VpKLAwPG1XI/AAAAAAAAAr8/S5AHH0jp2TM/2_thumb%25255B1%25255D_thumb%25255B2%25255D.png?imgmax=800)
